Weight Loss Drugs (Semaglutide)
Noor Alasady • May 26, 2023
Do These Drugs Work?
There has been a large hype and information about semaglutide in particular for those trying to lose weight. But overall, is it safe? And what are the consequences of this quick fix?
Semaglutide is a medication that belongs to the class of drugs known as glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists (GLP-1 RAs). It is primarily used for the treatment of type 2 diabetes, but it has also shown significant benefits in promoting weight loss.
The mechanism of action of semaglutide involves mimicking the effects of the hormone glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1), which is naturally produced in the gut. GLP-1 plays a crucial role in regulating blood sugar levels and appetite. It stimulates the release of insulin, reduces the production of glucagon (a hormone that raises blood sugar levels), slows down gastric emptying, and promotes a feeling of fullness.
By acting as a GLP-1 receptor agonist, semaglutide enhances these effects. When semaglutide is administered, it binds to GLP-1 receptors in various tissues, including the pancreas, brain, and gastrointestinal tract, exerting its beneficial effects.
Regarding weight loss, semaglutide has been found to have an impact on appetite control and food intake. It promotes satiety, leading to a reduced desire to eat and decreased hunger levels. Additionally, it slows down the emptying of the stomach, which prolongs the feeling of fullness after a meal. These effects can contribute to a decrease in overall calorie intake.
Furthermore, semaglutide has been shown to have an impact on body weight regulation and metabolism. It increases energy expenditure and promotes the utilization of stored fat for energy, leading to weight loss.
Clinical trials have demonstrated the efficacy of semaglutide in promoting weight loss. In addition to its primary use for diabetes management, higher doses of semaglutide have been approved for chronic weight management in individuals with a body mass index (BMI) of 30 or greater, or a BMI of 27 or greater with weight-related comorbidities.
These results are amazing, specifically for those with type 2 diabetes and those who are morbidly obese. But there are consequences for the average person who wants to take semaglutide just to lose 10 pounds for the Summer or a wedding.
The New England Journal of Medicine article "Tirzepatide versus Semaglutide Once Weekly in Type 2 Diabetes" reported on the effects of tirzepatide and semaglutide on weight loss and weight gain in patients with type 2 diabetes.
One important consideration when it comes to weight loss is the impact on muscle mass. Losing muscle mass can have negative consequences for overall health and can contribute to a decline in physical function, mobility, and quality of life.
While both tirzepatide and semaglutide were effective in promoting weight loss, it's important to note that some weight loss strategies can lead to a loss of muscle mass along with fat loss. This can be a particular concern for patients with type 2 diabetes, who may already be at risk for muscle loss due to age, inactivity, and other factors. It is of larger concern for those who use these agents for weight loss without diabetes, since the loss of mass muscle is detrimental to overall heatlth.
In the study, the researchers noted that maintaining muscle mass was an important consideration for patients taking semaglutide. They recommended that patients engage in regular physical activity and consume adequate amounts of protein to help maintain muscle mass while losing weight.
Additionally, patients should work closely with their healthcare providers to monitor their weight loss progress and adjust their treatment plan as needed to ensure that they are achieving their weight loss goals without losing too much muscle mass.
While weight loss is the ultimate goal, it's important to consider the impact on muscle mass and take steps to maintain muscle mass while losing weight. There are no magic pills and no quick fixes, one has to put in the effort to achieve the results in terms of weight loss and body muscle mass.
Share
Tweet
Share
Mail
Microneedling
By Noor Alasady
•
June 3, 2024
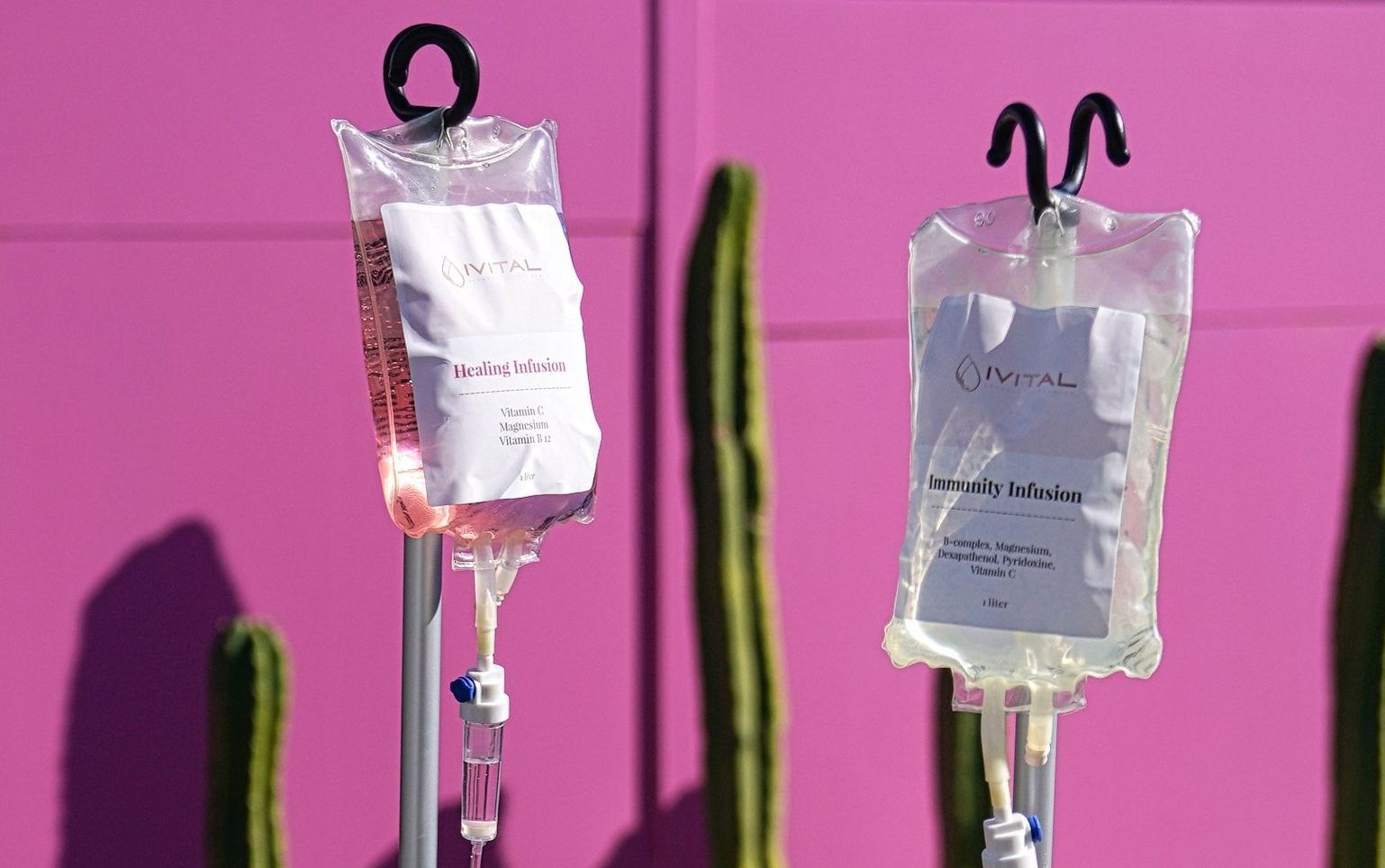
Hydration is the cornerstone of healthy skin, yet it's often overlooked in our daily routines. As the largest organ in our body, our skin needs adequate hydration to function optimally, maintain its elasticity, and keep that coveted glow. While drinking water is essential, sometimes our bodies need an extra boost, especially when faced with harsh environmental factors, stress, or intensive physical activities. That's where the specialized IV hydration products offered by Medispas, like our practice here at IVital Health, come into play.

By Noor Alasady
•
April 12, 2024
PRP “Platelet-rich plasma” Therapy, often called the “vampire facial,” involves using a patient’s blood to rejuvenate the skin and promote healing. With PRP, we can perform hair growth treatments, PRP facials, and PRP injections into nasolabial folds (the folds by the nose and cheeks) and/or marionette lines (lines below the sides of lips).
Disclaimer - The products and services provided by IVital, Inc are not intended to treat, diagnose, prevent or cure any illness or disease. The services provided on this website have not all been evaluated by the Food and Drug Administration. The information on this website is for educational purposes only and not intended as medical advice. Although IVital is run by professionals in their fields who have endeavored to formulate exceptional services and products to every individual, we still ask that you consult your physician before beginning any treatment or procedure.
© 2025
All Rights Reserved | IVital LLC.